When the agni becomes very weak, causing sluggish digestion, it is called Agnimandya.

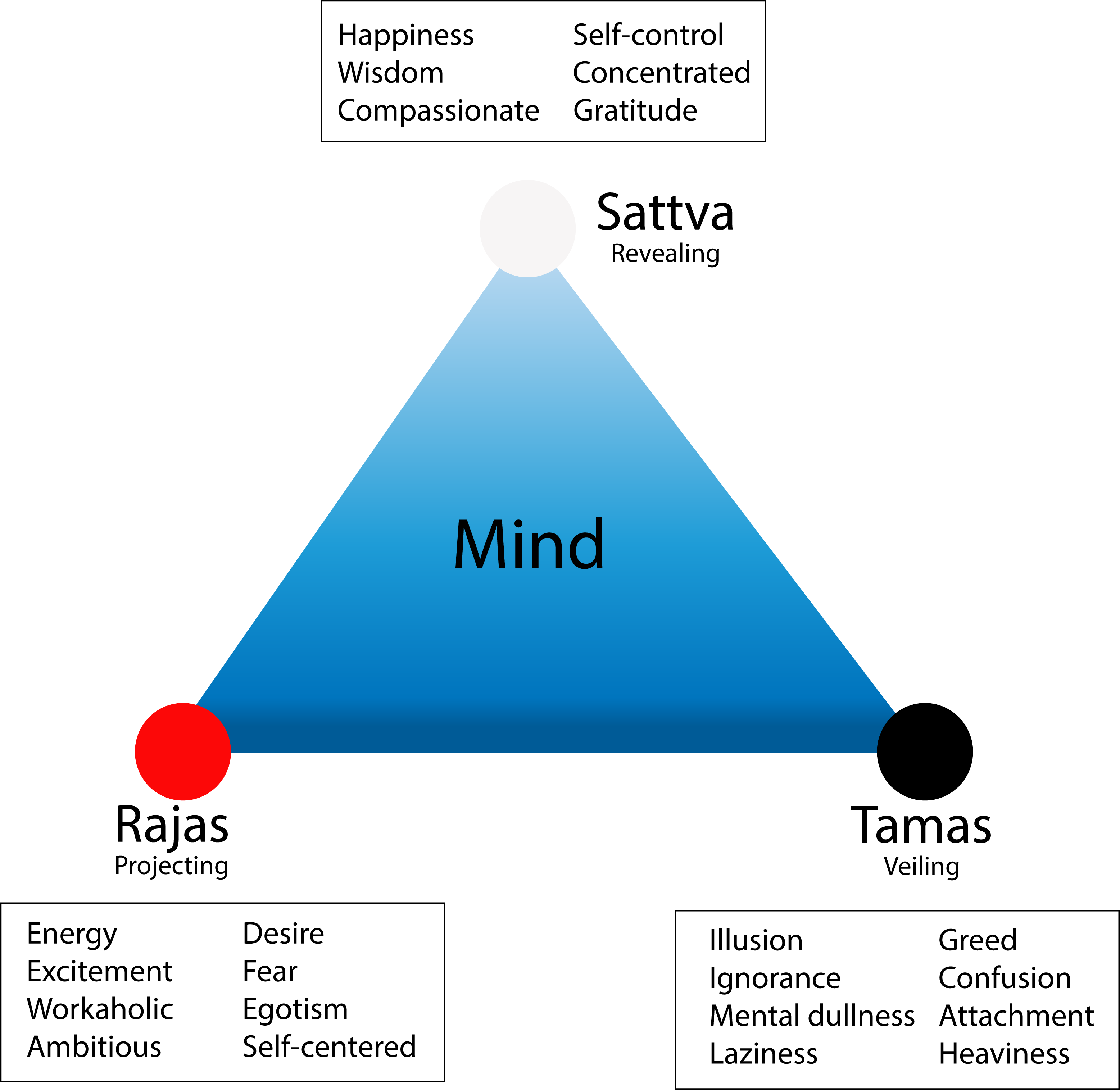
The Importance Of Agni And Good Digestion
Warning
The word ‘Agnimandya’ in its of itself signifies the state of inadequate process of digestion on ingested food. In Ayurveda there is a concept called Ama, which is considered as the main reason for majority of the diseases.
Types
Symptoms
Nidana – Causes
Purvarupa – Early/Premonitory/Mild Symptoms
Heaviness in the stomach, aversion to food, lethargy