Amla Benefits, Uses, Dosage and Side Effects
Dhatri: That which nurtures and supports the whole body like the Earth supports all living beings.
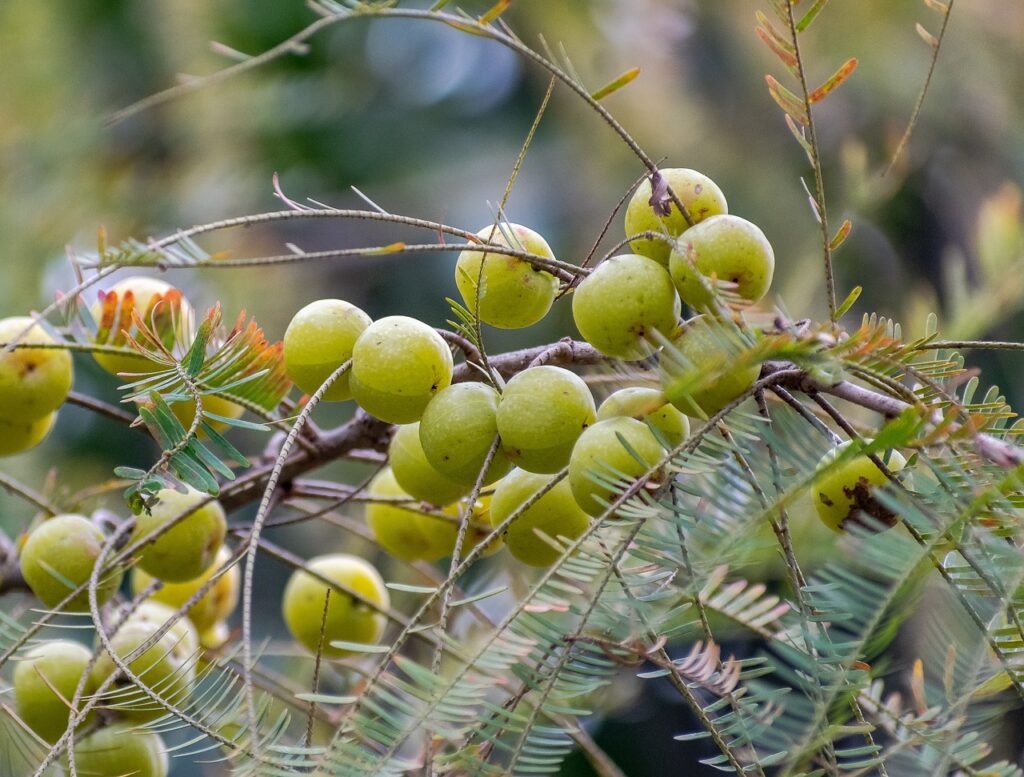
Names: Amalak, Amla, Dhatri, Emblica officinalis
Part Used: Fruit
Guna: Light, dry, cold
Rasa: All tastes except salty; Mainly sour
Vipaka: Sweet
Virya: Sita (Cooling)
Effect on Dosha: Pacifies all of the doshas, especially pitta
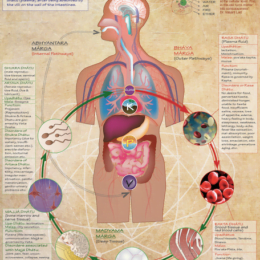
Main Action: Rejuvenator, aphrodisiac, laxative, hemostatic, antiaging; The world’s richest source of Vitamin C
Form Used: Decoction, infusion, powder, paste, juice
Locally: Paste applied on the forehead in pitta headaches, on the face to improve the complexion, and on blemishes on the skin, and the head for early graying.
Beneficial as a rasāyana: Nutritive to all of the dhātus, rejuvenating (E.g. Cyavanaprāśa).
Good for the digestive system: Used as agnidīpana, Āma pācana, anulomana in agnimāndya, acid reflux, ulcers, and liver diseases.
Used in pitta fever, burning sensation, skin problems, anemia, and diabetes.
Used in bleeding conditions such as bleeding gums, bleeding in the eyes, redness of the eyes, nose bleeds, bleeding hemorrhoids, and/or ulcers. Heals wounds.
Used as an aphrodisiac, for uterine debility, menorrhagia, and leucorrhea.