What Is Haritaki?
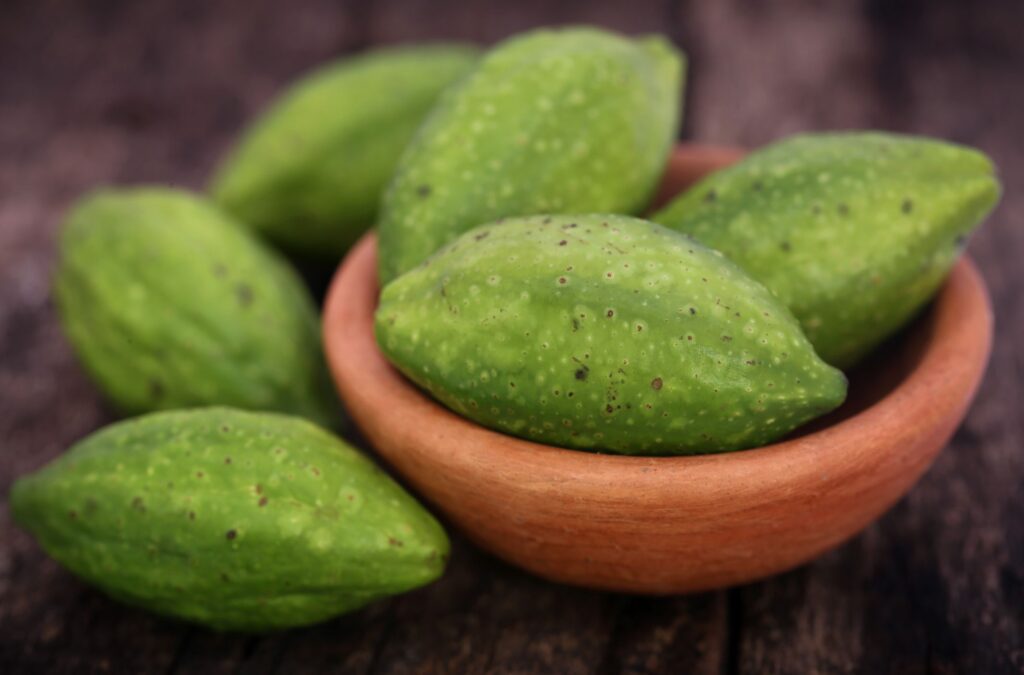
Haritaki (Chebulic myrobalan), also called Indian walnut or Indian hog plum, is a fruit that’s cultivated from the seeds of Terminalia chebula trees. The rind of the fruit is most often made into haritaki powder that has a number of medicinal uses, considering it acts as a natural laxative, has astringent properties and contains antioxidants.
Haritaki trees belong to the Combretaceae plant family and grow in tropical and subtropical regions, mostly throughout India, Nepal, China, Sri Lanka, Malaysia and Vietnam.
The fruit itself is drupe-shaped, has a hard green exterior and has ridges along its surface. Inside the flesh ranges from a yellow to orangish-brown color.
In addition to the fruit being valuable, different parts of the tree are also used for therapeutic purposes, including the roots, stems, barks, branches and leaves.
Names: Amalak, Amla, Dhatri, Emblica officinalis
Part Used: Fruit
Guna: Light, dry
Rasa: All except salty, mainly astringent
Vipaka: Sweet
Virya: Usna (Heating)
Effect on Dosha: Balances the tridoshas (mainly vata )
Main Action: Rejuvenative, laxative, anthelmintic, expectorant.
Popular Products: Triphala
Anupānas: It can be used in the spring with honey, in the summer with ghee and in the winter with raw sugar
Form Used: Powder, decoction paste
Contraindications: Physical weakness, pregnancy, dehydration, after severe exhaustion, after Pañcakarma
Hara: Eliminates, removes; One which removes malas, aggravated doshas and disease.
used to cleanse wounds and for gargling
weakness in the nervous system and brain.
reduce burning in the chest.
dhātuagni. Used to treat kaphaja skin diseases and prameha (diabetes).
and honey strengthen the eyes.
tea with honey reduces burning and help break kidney stones and flush them out of the
body.
of the dhātus. Works as an antiaging agent.
when used after food