The definition of Ama is that which is not transformed completely due to the weak Agni (digestive fire). Anything incompletely transformed is considered as in the state of Ama. Food that is not fully digested in the gut, or nutrients not completely metabolized and transformed into tissues in the body systems, or a fruit that does not ripen completely can come under the state of Ama. If we end up eating very heavy to digest foods, or in large quantities (more than what can be properly digested), or more often (frequent meals), then Samagni (normal digestive fire) in comparison becomes manda (weak), so may create Ama.
The resulting action of the Ama inside of the body is called Ama Dosha, which gives rise to various kinds of diseases and the root of all diseases.
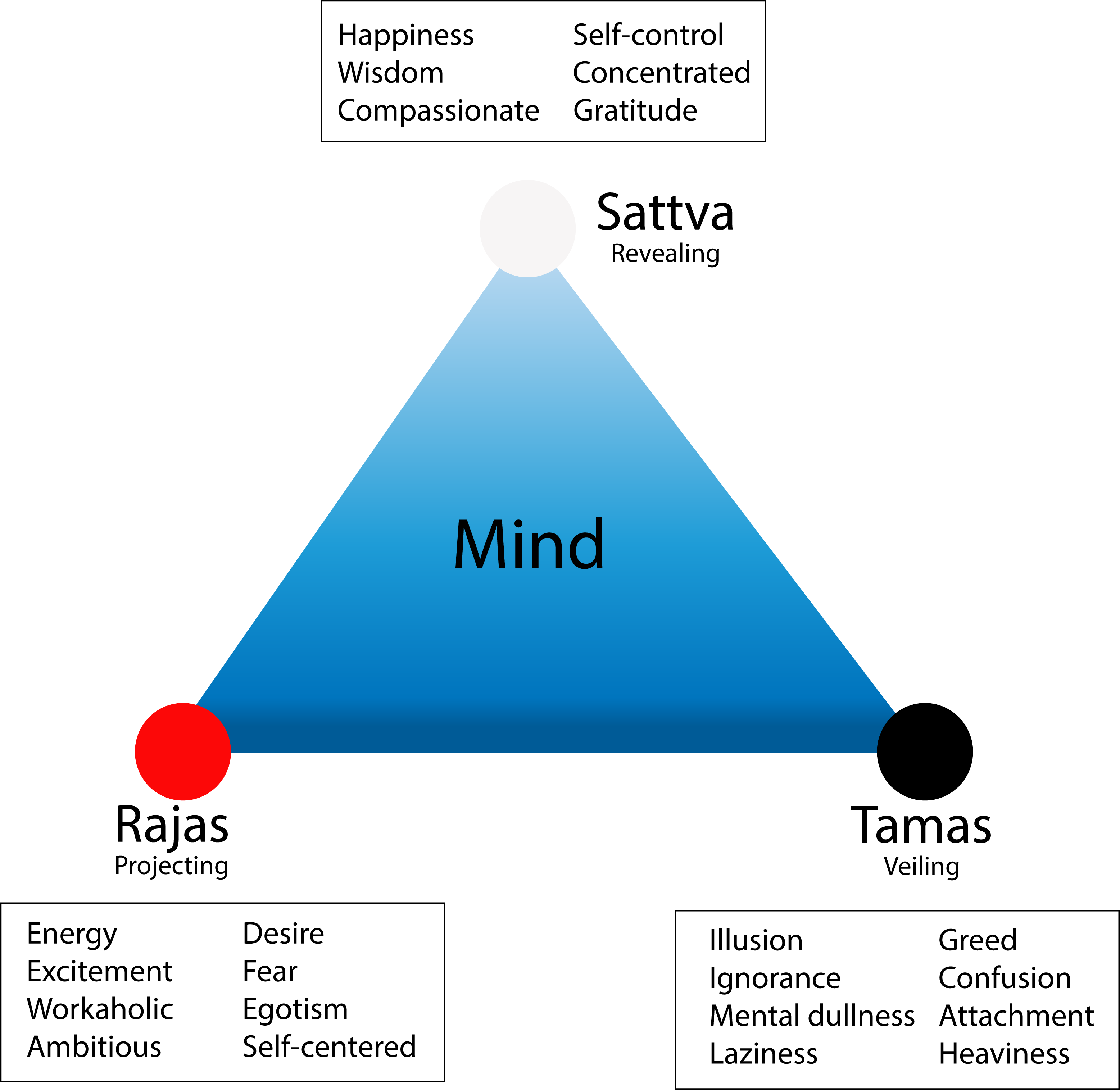
States of Disease
When there is Agni Māndya (weak Agni), Ama is produced.
● The state where Ama is present is called Sāma.
● The state where Ama is digested is called Nirāma.
It is important to know if the disease is at a Sāma or Nirāma state. The treatment will be different at both of these stages. In the Sāma state, pungent bitter herbs need to be used to digest Ama. In the Nirāma state Dhātu building herbs need to be used to strengthen the Dhātus .
Sama and Nirama Vata/Pitta/Kapha
When a Dosha is associated with Ama it is called Sama Vata/Pitta/Kapha. To treat the Dosha, the Ama should be tackled first.
The association of Ama with a Dosha should be broken by the administration of Deepana (fire kindling medicines or medicines which enhance the appetite and enhance the digestion capacity, correct metabolic process in presence of sluggish digestion) and Pachana or Ama Pachana Dravyas (medicines which digest and expel Ama).
When Ama loses its association with a Dosha, it will be called Nirama Vata/Pitta/Kapha. Though the pathological element in the form of Ama has been separated from a Dosha, the free Dosha is still pathological, since it is also in vitiated form. This Dosha should be handled by the administration of alleviating or expelling treatments and medicines treatments.
Causes of Ama:

Signs of Ama

Signs of Sama Vata
Symptoms of disturbances in the functions of the energy Vata (Sama Vata), which are due to the presence of Ama in the body, are:
- Constipation
- Bloating
- Gurgling in the abdomen
- Pain in the lower abdomen, back and sides
- Pricking pain in the body

Signs of Sama Pitta
Signs of disturbances in the functions of the Pitta energy (Sama Pitta), which are due to the presence of Ama in the body, are:
- Sour belching
- Vomiting green
- Strong, acidic-smelling pitta
- Burning pain in chest and throat
Signs of Sama Kapha
Signs of disturbances in the functions of the Kapha energy (Sama Kapha), which are due to the presence of Ama in the body, are:
- Cloudy, white phlegm
- Very sticky, thick mucus
- Bad breath
- Increased turbidity in urine

Sama Purisha (stool)
Here, when defecating, there are symptoms such as:
- Abundant amount
- Unpleasant odor
- Lack of form
- Immersion in water (Sinks instead of floating)
The absence of such anomalies is called Nirama purish and is considered the norm in defecation.
Sama Mutra (urine)
In this condition, when urinating are observed:
- Turbid urine
- Larger amount and higher density than normal
- Unpleasant odor
With Nirama puris, the urine is clean, clear, odorless and with a normal amount and density.
How do I prevent Ama?
- Avoid overeating and/or eating heavy foods in large quantities.
- Avoid tamasic foods. Examples: Leftovers, processed, canned foods, fast food or food with additives and colorings.
- Avoid ice cold water and drinks and cold foods.
- Eat warm, freshly cooked food.
- Make lunch your main meal and eat a light breakfast and dinner.
- Eat heavy foods in smaller quantities and light foods more.
- Calm the mind before eating.

How do I treat Ama?
- Fasting: Skip a meal or eat a fruit
- Drink warm water, eat clear soups
- Use digesting herbs such as ginger black pepper, cumin seeds and garlic
- In chronic cases, do Panchakarma

Visit a Holistic Ayurvedic Coach
After the appropriate diagnosis, the Holistic Ayurvedic Coach may recommend programs that affect both the causes of the formation of Ama and the consequences.

Free 60 Minute Consultation
Completely free of charge, 60 Minute Consultation

Dietary Advise
Advise on dietary choices based on Doshas and the six tastes

Daily Routines
Create daily and nightly routines based on constitution, age and the seasons

Ayurvedic Principles
Ayurvedic principles including the holistic view of health, the elements, Doshas

Location
Online meeting, phone call or in person at coffee shop/park nearby Charlottesville, VA

Yoga Advise
Recommend yoga and yogic practices for improved health, including pranayama/breathwork